Twitter, 11/15/2021, 7:42 a.m. [Time zone? Who knows.]
A German satellite watcher says Russia hit one of its own old spy satellites, Kosmos 1408, with a missile and blew it to bits. I wanted to say “blew it out of the sky” but the satellite was of course in orbit so the exploded bits don’t fall down, they stay in the sky, still orbiting.
The German watcher says 14 bits, debris objects, have been tracked and though “my unofficial source has been pretty reliable on topics like this in the past,” the whole event is still unconfirmed. An American satellite watcher who’s also an astronomer adds that Kosmos 1408 was, and all its pieces might be, in a 465 x 490 km orbit. The debris, he added, will almost certainly intersect with the orbit of the International Space.
And, as it turns out, the ISS crew had already been told to expect eight minutes-worth of “debris field transit,” to get out of the space station and into their little lifeboat modules, every 93 minutes. NASA later posts an audio with the usual flat, factual voices, “ Hey Mark, good morning sorry for the early call, we were recently informed of a satellite breakup, need you to review safe haven procedure; read back; that’s a good read, we’ll let you know when to start; sounds good,” and another flat voice says, “thanks for the heads-up.”
And finally confirmation: a newspaper space reporter writes that a commercial satellite company called LeoLabs “spots a field of objects where the Kosmos 1408 satellite used to be.” The U.S. Space Command issues a press release, saying it’s working on it and it’s notifying everybody else with satellites not all of which can maneuver out of the way.
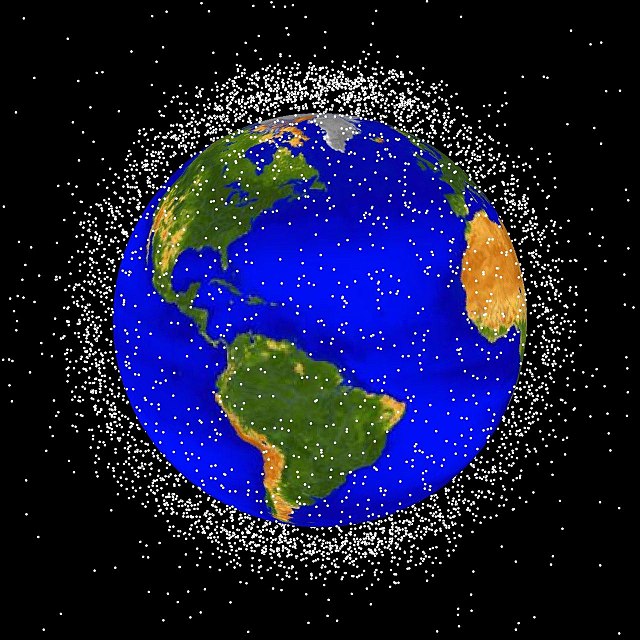
Then a good fraction of Twitter notes that other countries, including ours, have done this kind of satellite skeet shooting before, which accounts for the million billion gazillion pieces of debris going over 17,000 mph, circling the earth like a giant cloud of bats out of hell. If you run into one of these bats, depending on its size, it can either knock a hole in you or turn you into another debris event.
This kind of thing is against the rules which are more like “we really should avoid doing these kinds of things shouldn’t we” than they are enforceable regulations in real treaties. Turns out neither the U.S. nor Russia can get treaty discussions on their busy calendars.
Information slowly pings into Twitter: Kosmos 1408 was an electronic signals intelligence satellite launched in 1982 and has been dead for decades, the missile came from Russia’s launch site at Plesetsk. For a while Twitter, some of it writing in Cyrillic, wasn’t sure whether the missile launch, the tracked debris, and space station alert were all part of the same story but eventually settled on, yes, they are, and said an American space policy expert, “it was beyond irresponsible for Russia to do this.” Later the same expert, seeing evidence that Russia had announced the missile launch, said “well shit.” Twitter now fills up with national security (natsec) writers linking to articles they’d written several years ago saying exactly this kind of thing might happen.
The satellite watchers discuss the size of Kosmos 1408 – huge – and the amount of debris it broke up into and how big the pieces are and what percentage of the pieces are too small to track but big enough to hurt. They think the debris will stay up there for 6 months to a year, some of it up to 10 years. They note that some of this debris can get kicked up to very high orbit where it will see little reason to come down. Another space policy expert says that over 600 other satellites are in the same orbit as the debris, and that the space station has actually had to move. The State Department enters the room, using the words, “recklessly” “dangerous,” “irresponsible,” “disingenuous,” and “hypocritical.” A space news reporter says the State Department also says it won’t tolerate Russian actions but won’t say what “not tolerate” means.
Natsec writers who have been on this beat since shortly after there were satellites, link to more articles. Apparently the missile, a kind named Nudol, has been tested 10 times before but never actually blew up a satellite and a Russia expert suspects that maybe Russia just wanted to know if Nudol could do what it was designed to. The Russia expert also says “It’s not as if they didn’t know where the debris will end up. Or as if nobody could predict the kind of backlash that Russia is definitely going to get.” A different Russia expert says that anyone surprised by this hasn’t been paying attention for the last 20 years.
An academic tweets a simulation of how Kosmos 1408’s debris field will evolve with time. A little bright splot arcing over the earth gets stretched out into a bright fuzzy line, which develops a tail that gets longer and longer and increasingly breaks up, the pieces at first aligning with each other, then aligning less and less and starting to wander into a self-colliding, self-perpetuating cloud. One of the Russia experts asks if anyone has yet pointed out that the whole event is probably Russia’s response to what’s going on at the Ukrainian border? “Someone must have,” he says. An astronomer says, “This seems . . . really bad?” Another one says, “At least it’s slightly lower than HST,” the Hubble Space Telescope.
A newspaper reporter talked to the head of NASA who said he didn’t think the Russian space agency, Roscosmos, knew anything about this and are probably appalled – after all some the the ISS crew trying to get out of the way were Russian.
Twitter, 11/16/2021
The astronomer/satellite watcher says he suspects the smaller bits are already “littering Starlink orbits.” A Russian natsec writer quotes a Russian news story quoting a Russian general saying it was “no big deal, did not violate anything, and now US military will be able to push for more money.” An American natsec writer quotes TASS quoting the Russian defense minister saying, “It hit an old satellite with precision worthy of a goldsmith. The remaining debris pose no threats to space activity.” The Russian writer reports on a Russian simulation of the debris cloud, showing the path of a single white dot intersecting with a single blue dot but not at the same time and well above it. The Russian policy expert tweets that if the cartoonish simulation is the best the Russian Ministry of Defense could do, it should count on not being taken seriously, not that it cares. An American natsec writer answers, “For realz,” and adds a rolling-eye emoji.
American senators and the British space agency tweet concern etc. The Russian policy expert says to keep in mind that Russia isn’t really interested in destroying US military satellites, it’s mostly worried about US weapons that can hit Russian targets on the ground and in space. The head of NASA tweets that he expressed dismay to the head of the Russian space agency, who tweeted something in Cyrillic that was translated as “there’s no point in yelling at me,” and the NASA head said they agreed to move past blame and make joint plans for how to dodge 1500 pieces of space debris for decades. An American natsec expert tweets that he doesn’t think it’s a coincidence that Russia is now massing troops on Ukraine’s border, and the Russian policy expert tweets, “I knew it, I knew it!” The EU tweeted concern. Various tweets discuss whether the lack of rules for a space war might be compensated for by norms, and how countries could define bad anti-satellite missiles against good missile defense. These tweets could have been preserved whole from the 1980s.
Twitter, 11/17/2021
The UK has tweeted concern, and an academic military historian quotes a Russian diplomat telling the UK, “Besides, look. You together with the US blocked negotiations. At the same time US left no doubt that it was going to weaponise outer space. Did you really believe that under the circumstances Russia would refrain from developing technologies to counter this threat?” Replies to that tweet pointed out that the same argument has been going on since the Reagan administration.
The U.S. Space Command links to the opening scene of Gravity, with the ISS blown to photogenic bits and Sandra Bullock tumbling helplessly in space. A lot of tweets invoke the Kessler Effect and I will steadfastly not look that up, I can figure it out.
Twitter, 11/18/2021
The commercial space company says that Kosmos 1408 was less than 100 km above the ISS and 100 km below many satellite constellations. It added a little graph showing the debris spreading out between 300 and 800 km. It said it was tracking 253 pieces, likely the largest ones, and that the total number of trackable pieces should be between 1250 and 2500. They said they’d start generating “conjuction messages.” Reuters said that China said it was too early to comment.
Twitter 11/19/2021, 11/20/2021
Twitter has moved on. The debris cloud got bigger and went higher. Twitter discussed whether the missile hit the satellite from behind or head-on. An American academic referred to the commercial satellite companies’ latest simulation and tweeted, “The whole episode is bad news.”



The point being that 1) this is just the most recent in a long line of small, nasty battles in the long-simmering Space War I wrote about a while back; 2) peace through diplomacy either isn’t working or is working too slowly to keep up; 3) so this kind of thing will keep happening. The other point is, 4) it’s an excuse for me to wander around the satellite watchers again, the hobbyists who aren’t paid or commissioned, who watch satellites because why wouldn’t they, and who publish it all so the rest of us knows what’s going on. And the point after that is, 5) Twitter turns out to be a remarkably good source for reporting the news about satellite watching. I did nothing, called no one, just sat on the couch reading Twitter. And given the lack of reporting and fact-checking, and the general Twitter-credibility, this post is surprisingly not-wrong.
UPDATE: 11/30/2021: A Brit satellite watcher says that the orbits of the trackable pieces don’t intersect China’s space station but are “closer to the danger zone” for the ISS. And a space reporter says that some Starlinks have had to dodge debris. And NASA announced that it had cancelled the astronauts’ space walk from the ISS because of the possibility of debris, though it declined to speculate whether the debris was from Kosmos 1408. One of these fine days, this is going to stop being funny.
__________
Picture credit: NASA. It’s real data, that stuff is really all up there.
